上篇文件,主要是把集群服务器状态同步到一台机器上,然后通过grep,awk 什么的比较方便。但是考虑到更简单,方便的操作,那就是接入elk日志管理平台
来来,大致思路很简单
(1)有个完成的elk集群
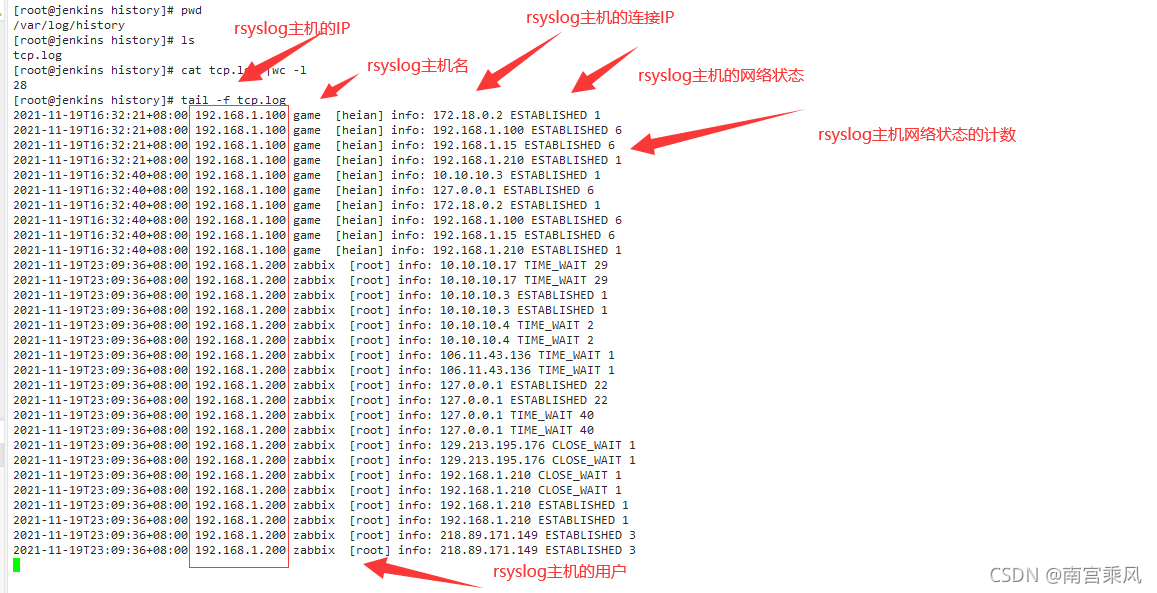
(2)使用filebeat收集汇总的tcp.log(只要一个filebeat就可以)
(3)把filebeat数据发送到logstash中,进行日志切割转换(靠,正则很难受)
(4)把logstash的数据存储到es
(5)kibana展示es中的数据日志
(1)filebeat收集tcp.log
来来,看配置,很简单
配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
[root@logserver01 filebeat]# cat tcp_listen.yml
#=========================== Filebeat inputs =============================
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
tail_files: true
paths:
- /var/log/history/tcp.log
#=========================== Filebeat outppp_id: messuts =============================
output.logstash:
hosts: ["127.0.0.1:5516"]
|
启动命令
1
|
nohup /usr/local/filebeat/filebeat -e -c /usr/local/filebeat/tcp_listen.yml -path.data=/usr/local/filebeat/tcp_listen &
|
(2)logstash收集清洗日志
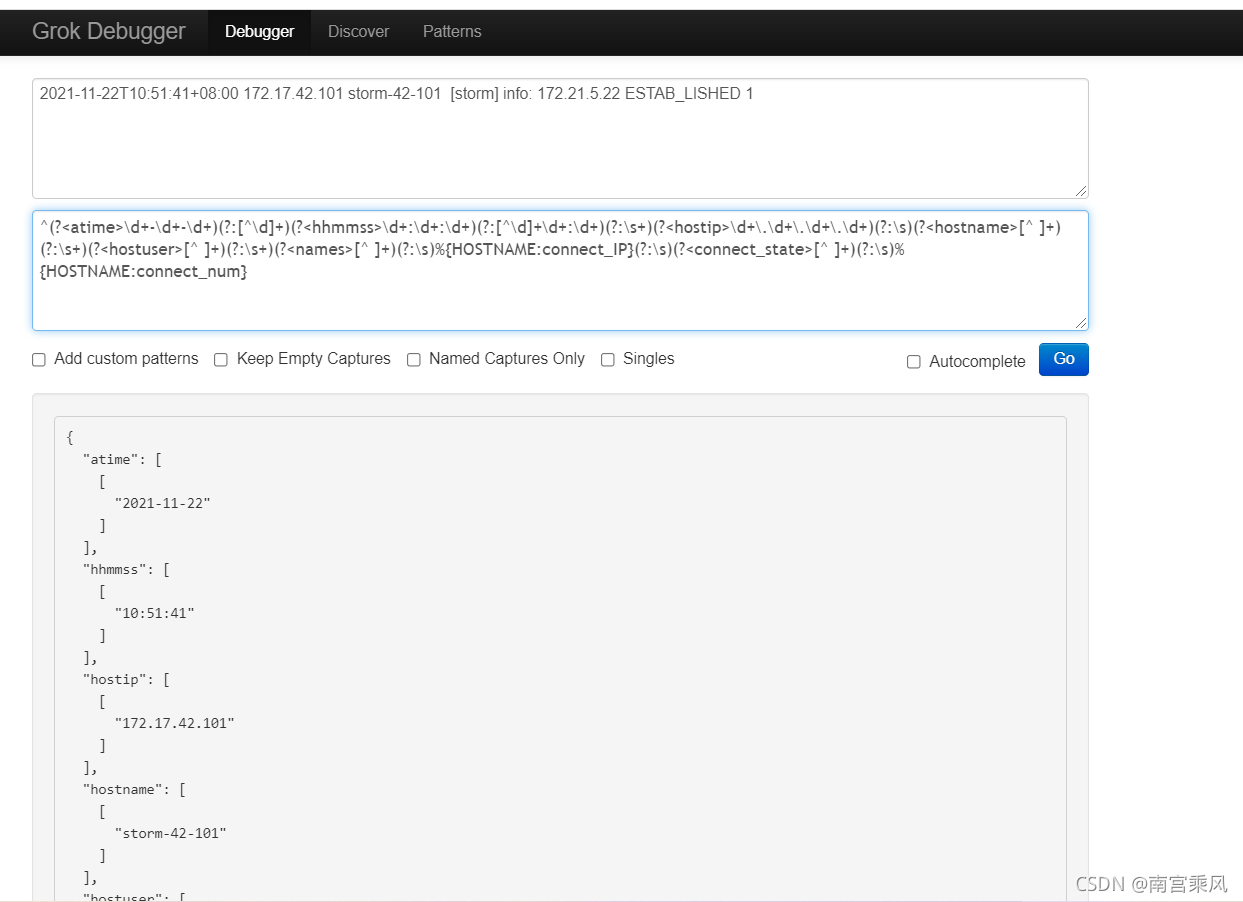
清洗日志,比较麻烦,需要grok正则来实现
grok正则
http://grokdebug.herokuapp.com/
1
|
2021-11-22T10:51:41+08:00 172.17.42.101 storm-42-101 [storm] info: 172.21.5.22 ESTABLISHED 1
|
grok的正则
1
|
^(?<atime>\d+-\d+-\d+)(?:[^\d]+)(?<hhmmss>\d+:\d+:\d+)(?:[^\d]+\d+:\d+)(?:\s+)(?<hostip>\d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+)(?:\s)(?<hostname>[^ ]+)(?:\s+)(?<hostuser>[^ ]+)(?:\s+)(?<names>[^ ]+)(?:\s)%{HOSTNAME:connect_IP}(?:\s)(?<connect_state>[^ ]+)(?:\s)%{HOSTNAME:connect_num}
|
配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
[root@logserver01 config]# cat tcp_listen.conf
input {
beats {
port => 5516
type => syslog
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => {
"message" => "^(?<atime>\d+-\d+-\d+)(?:[^\d]+)(?<hhmmss>\d+:\d+:\d+)(?:[^\d]+\d+:\d+)(?:\s+)(?<hostip>\d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+)(?:\s)(?<hostname>[^ ]+)(?:\s+)(?<hostuser>[^ ]+)(?:\s+)(?<names>[^ ]+)(?:\s)%{HOSTNAME:connect_IP}(?:\s)(?<connect_state>[^ ]+)(?:\s)%{HOSTNAME:connect_num}"
}
overwrite => ["message"]
}
mutate {
split => ["type",","]
}
mutate{remove_field => [ "tags","agent","host","log","ecs","type" ]}
ruby {
code => "event.set('index_date', event.get('@timestamp').time.localtime + 8*60*60)"
}
mutate {
convert => ["index_date", "string"]
gsub => ["index_date", "-\d{2}T([\S\s]*?)Z", ""]
gsub => ["index_date", "-", "."]
}
date {
match => ["time", "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS", "UNIX"]
target => "@timestamp"
locale => "cn"
}
}
output {
stdout {
# codec=> rubydebug
}
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://127.0.0.1:9200"]
index => "tcp_listen_%{index_date}"
}
}
|
启动命令
1
|
nohup /usr/local/logstash/bin/logstash -f /usr/local/logstash/config/tcp_listen.conf --path.data=/usr/local/logstash/data/tcp_listen &
|
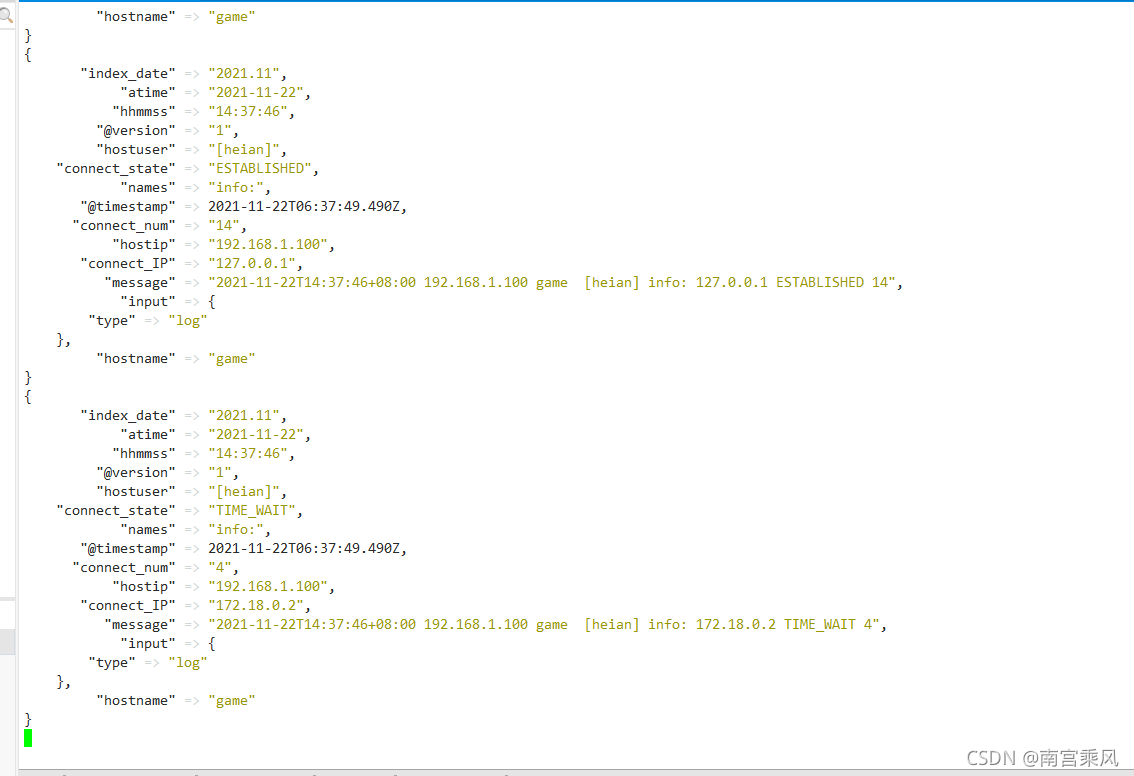
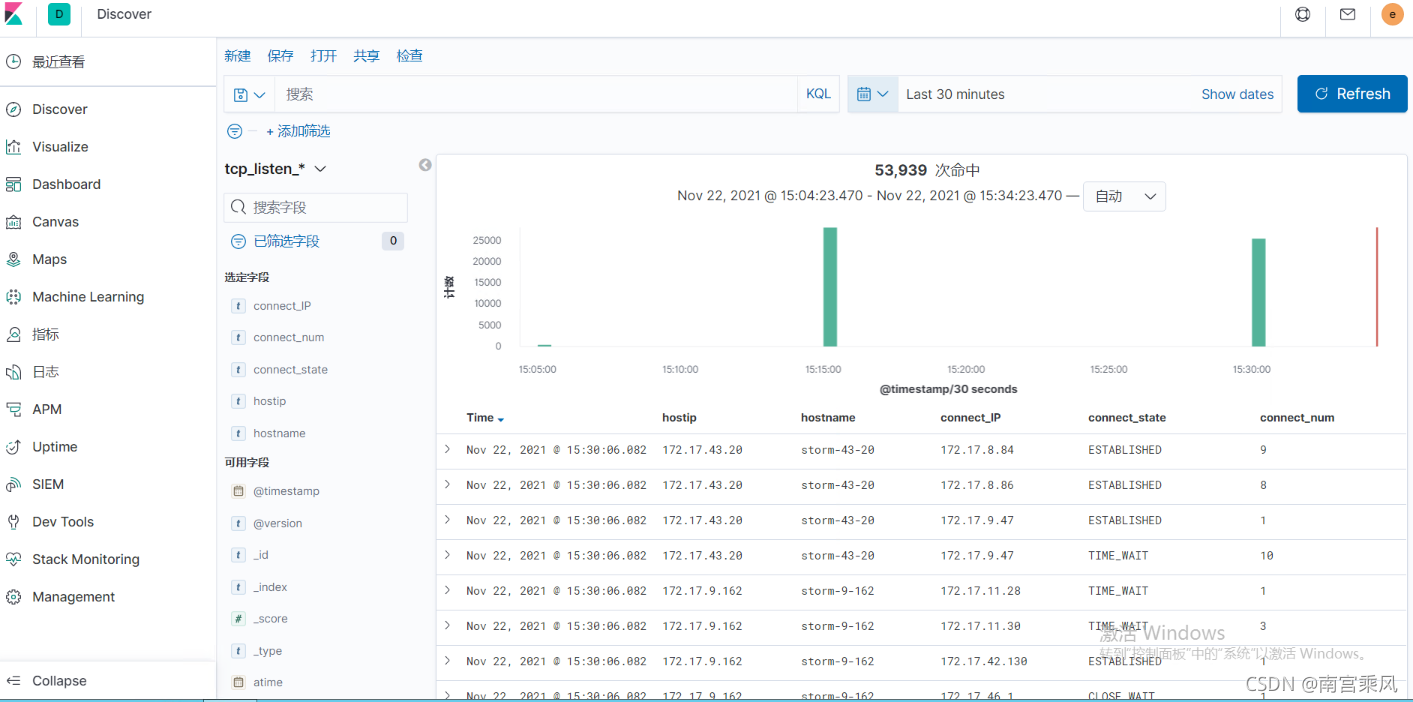
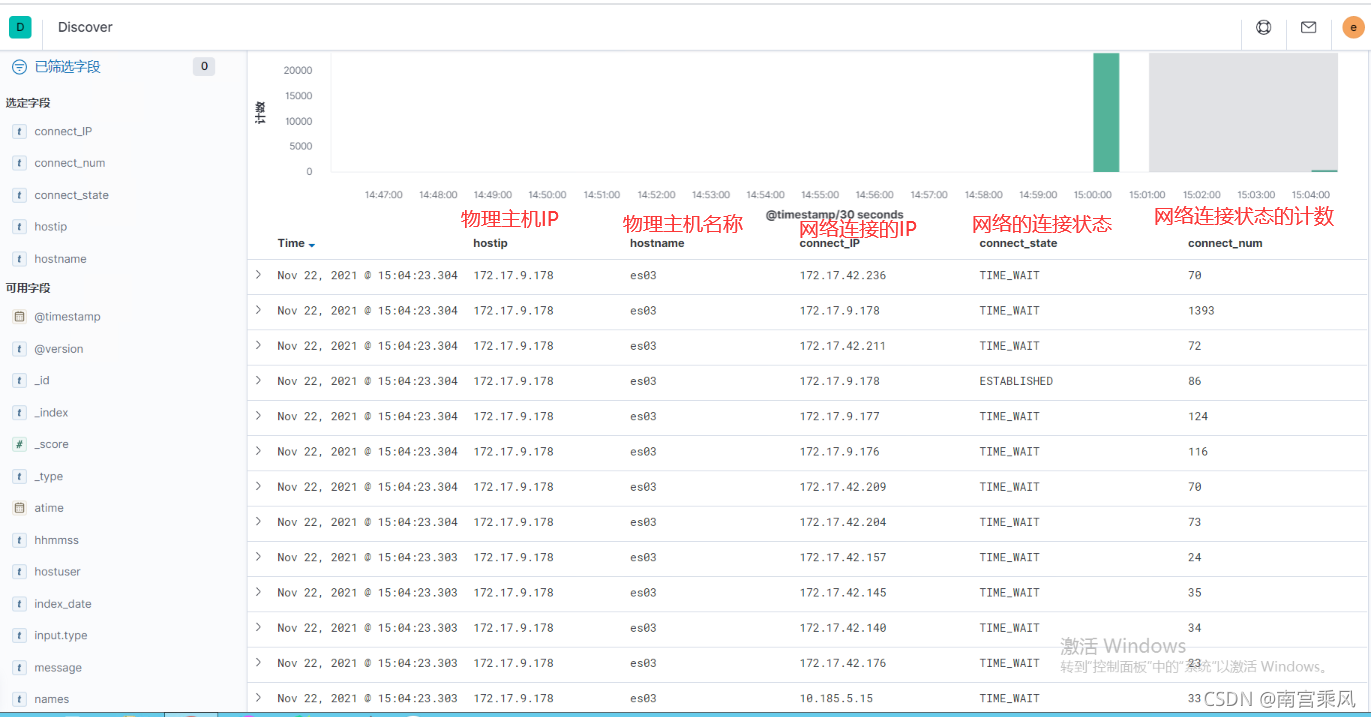
(3)kibana展示数据
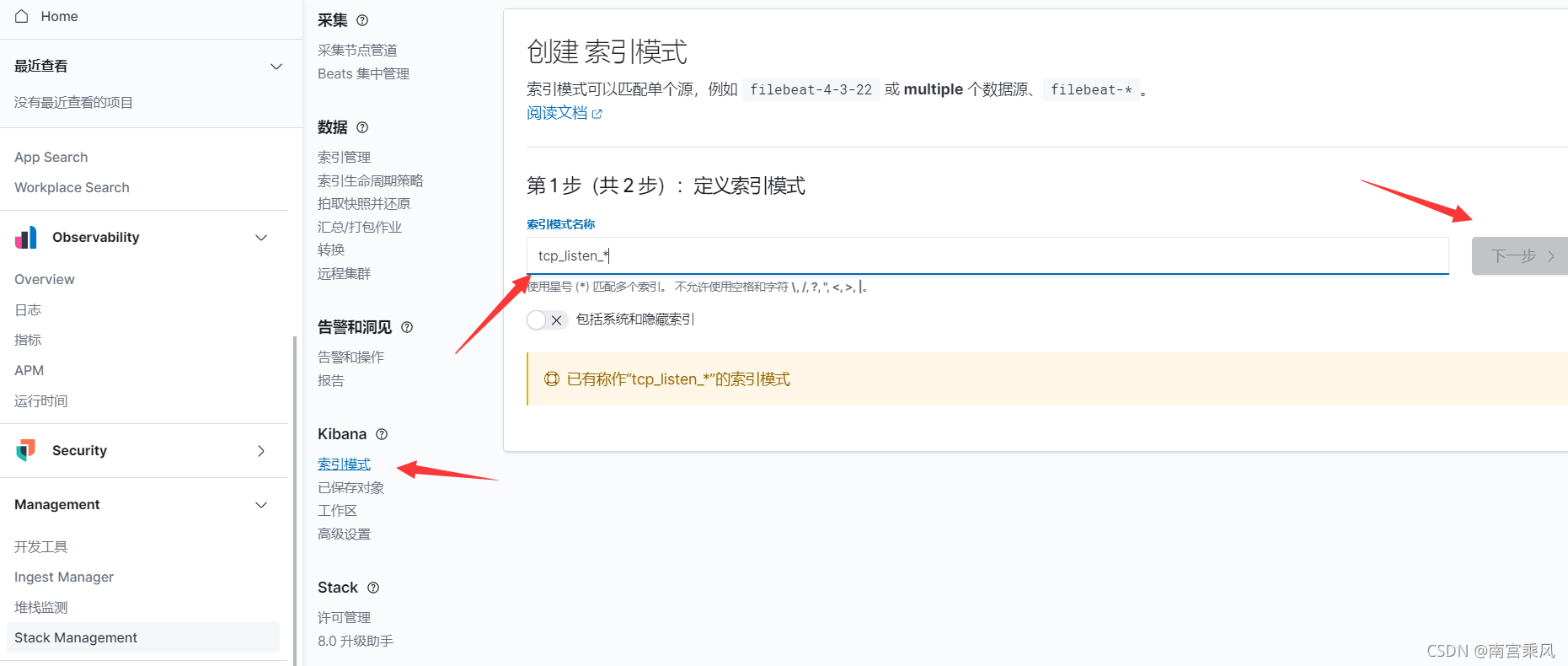
创建索引
查看数据
脚本为15分钟拉去一次数据的。所有在kibana展示也是和脚本时间同步的